- Monday - Saturday 10:00 AM - 5:00 PM
- Call us: +91 7736 00 7326


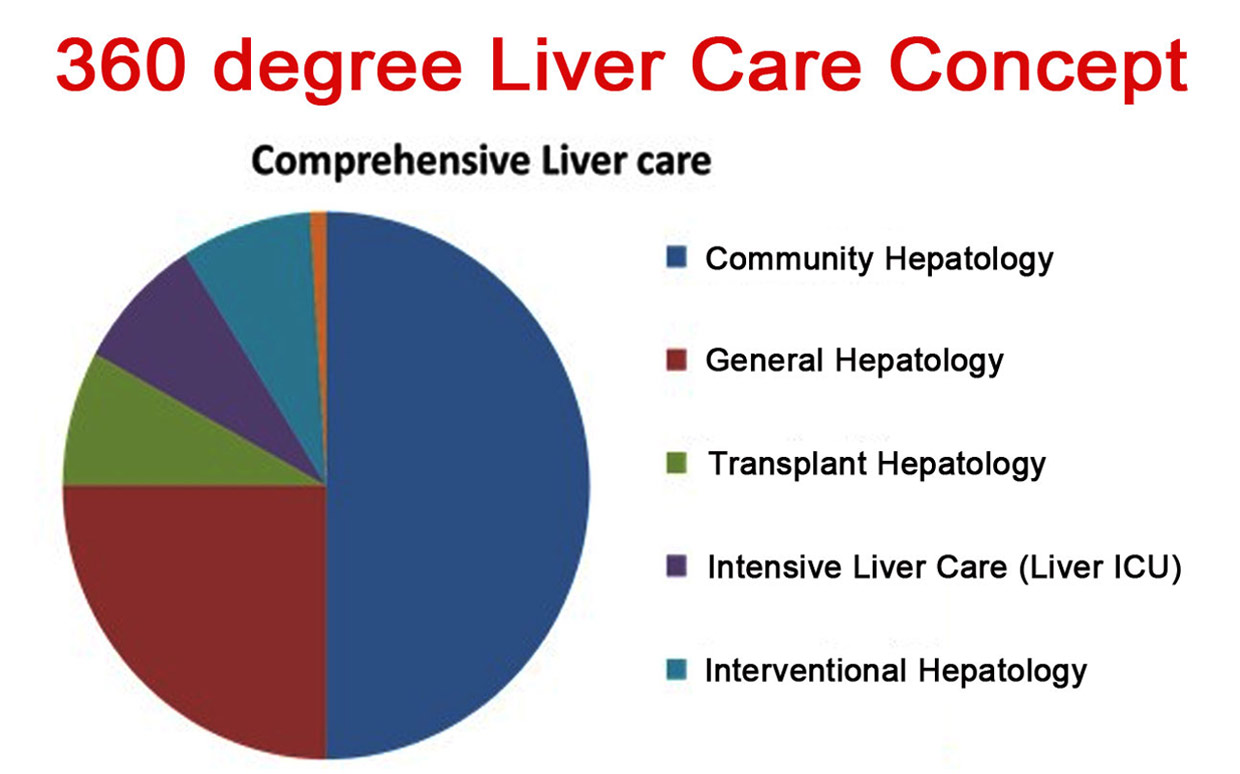
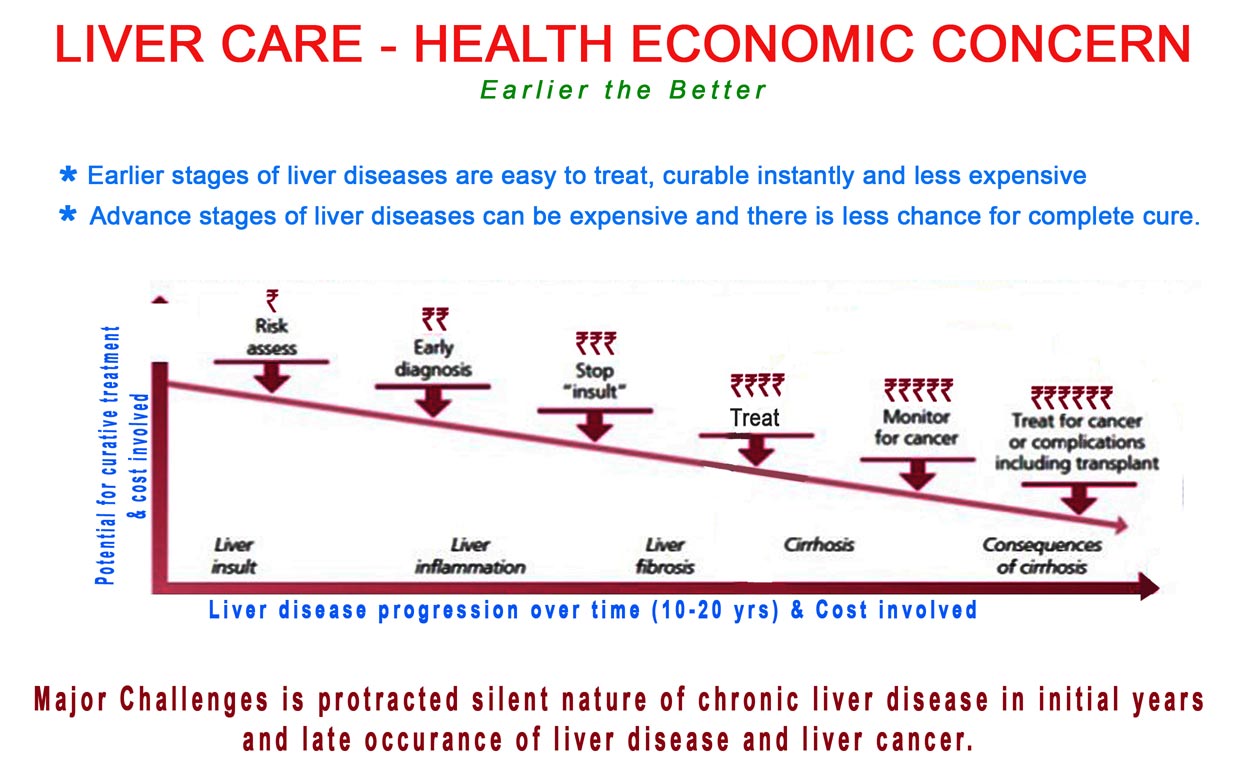
Hepatology is a medical field dedicated to studying, diagnosing, and treating liver, gallbladder, bile ducts, and pancreas disorders.
People consult a hepatologist for conditions like hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, fatty liver disease, liver cancer, or any signs of liver dysfunction, such as jaundice or unexplained abdominal pain.
Common diseases in hepatology include hepatitis (A, B, and C), fatty liver disease, cirrhosis, liver cancer, and bile duct disorders.
Hepatologists use blood tests, liver function tests, imaging like ultrasounds, CT scans, and sometimes liver biopsies to diagnose liver diseases.
Hepatology is essential in diagnosing and managing hepatitis, focusing on reducing liver inflammation, preventing progression, and managing symptoms.
In hepatology, liver cancer treatment depends on the stage and may include surgery, liver transplants, chemotherapy, or targeted therapies, often involving a multidisciplinary approach.
Hepatologists typically recommend a balanced diet, reducing alcohol, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding hepatitis infections through vaccination and safe practices.
Liver function tests are central to hepatology, providing crucial information about liver health, detecting inflammation, and guiding treatment plans.
Yes, hepatology addresses genetic liver disorders, such as Wilson’s disease or hemochromatosis, through monitoring, lifestyle guidance, and specific treatments.
Hepatology plays a key role in assessing candidates for liver transplants, preparing patients, and providing post-transplant care.
Advancements in hepatology, like targeted therapies, minimally invasive diagnostics, and improved liver transplant techniques, have significantly enhanced patient outcomes in liver disease management.
FB page